Creating a Condition File Using the Graphical User Interface¶
A user may construct the condition.txt file by hand or by using the Graphical User Interface.
Launching the Graphical User Interface¶
First, change to the directory where you want the output files to be stored; for the following example, we will store the output in the directory run, located in the $RMG directory.
For Linux users, run the following commands to launch the GUI:
cd $RMG/run
java -Xmx500m -classpath $RMG/bin/RMG.jar GUI > output &
For Windows users, run the following commands to launch the GUI:
cd "%rmg%\run"
java -Xmx500m -classpath "%rmg%\bin\RMG.jar" GUI > output &
The “Initial Conditions” tab¶
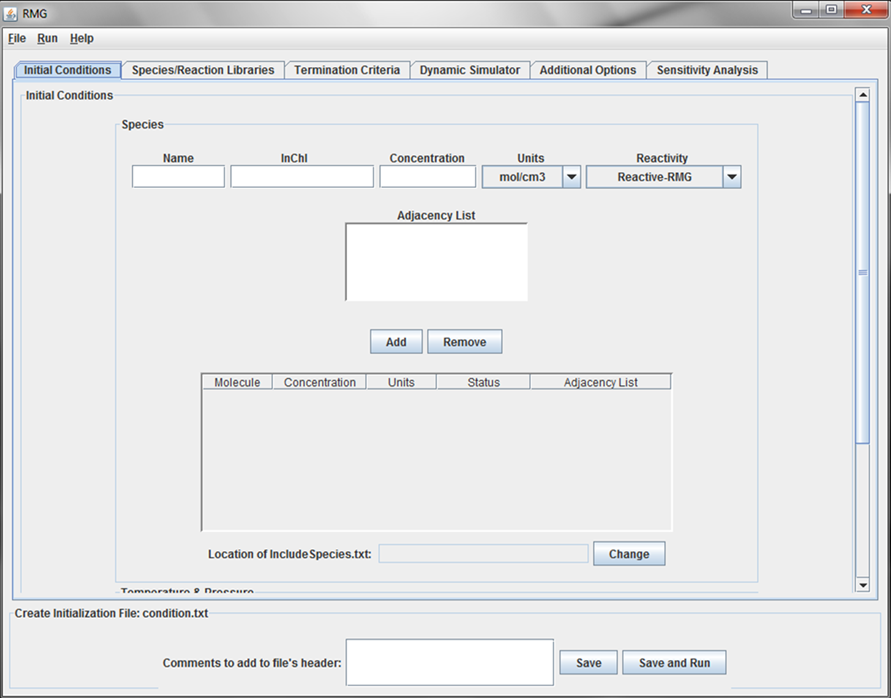
Initial Conditions tab
This tab of the GUI allows the user to enter the Reactants, Inert Gases, and Initial Conditions for the simulation.
Reactants and Inert Gases¶
For each species, a “Name,” “Concentration,” “Units,” and “Reactivity” must be specified. The three options for “Reactivity” are:
- “Inert” - a species for which RMG will not build a reaction mechanism
- “Reactive-User” - a species for which RMG will build a mechanism, but only according to the list of reactions the user has provided
- “Reactive-RMG” - a species for which RMG will build a mechanism, according to the reaction family templates located in the RMG_database/kinetics folder
If the species is selected as “Inert”, no structural information for the molecule is necessary. RMG only recognizes the following Inerts: N2, He, Ne, Ar.
If the species is selected as either “Reactive-User” or “Reactive-RMG”, the user must supply structural information about the molecule. This information may be provided in one of three ways: adjacency list, InChI, or .mol file.
An example of an adjacency list (for methane) is:
1 C 0 {2,S} {3,S} {4,S} {5,S}
2 H 0 {1,S}
3 H 0 {1,S}
4 H 0 {1,S}
5 H 0 {1,S}
An equally valid adjacency list for methane (with the Hydrogen atoms removed) is:
1 C 0
If the user knows the InChI of the molecule (and the InChI executable is located in the RMG/bin/ folder), the GUI will convert the InChI to an adjacency list upon pushing the “Add” button. If using either InChI software version 1.01 or software version 1.02beta, the InChI for methane is:
InChI=1/CH4/h1H4
However, if using the InChI software version 1.02 for Standard InChI/InChIKey, the InChI for methane is:
InChI=1S/CH4/h1H4
Please make sure the InChI you pass to the RMG GUI is consistent with the InChI version located in the $RMG\bin\ folder. Upon pushing the “Add” button, if neither an adjacency list nor InChI have been provided, the GUI will ask the user for the location of the .mol file associated with this species. If the InChI executable is in the proper folder, the GUI will convert the .mol file to an adjacency list.
The user may add/remove species to the model by clicking the appropriate buttons.
Reactive-User Species¶
If a “Reactive-User” species is added to the model, the GUI will ask the user for the location of the IncludeSpecies.txt file. If no “Reactive-User” species are added to the model, the “Location of IncludeSpecies.txt” field will remain inactive.
Initial Conditions¶
RMG currently only has one pressure/temperature model: “Constant”. However, the user may specify a list of temperatures and pressures for which to build the reaction mechanism. The list of temperatures (or pressures) should be separated from one another with a blank space or a return carriage.
The “Species/Reactions Libraries” tab¶
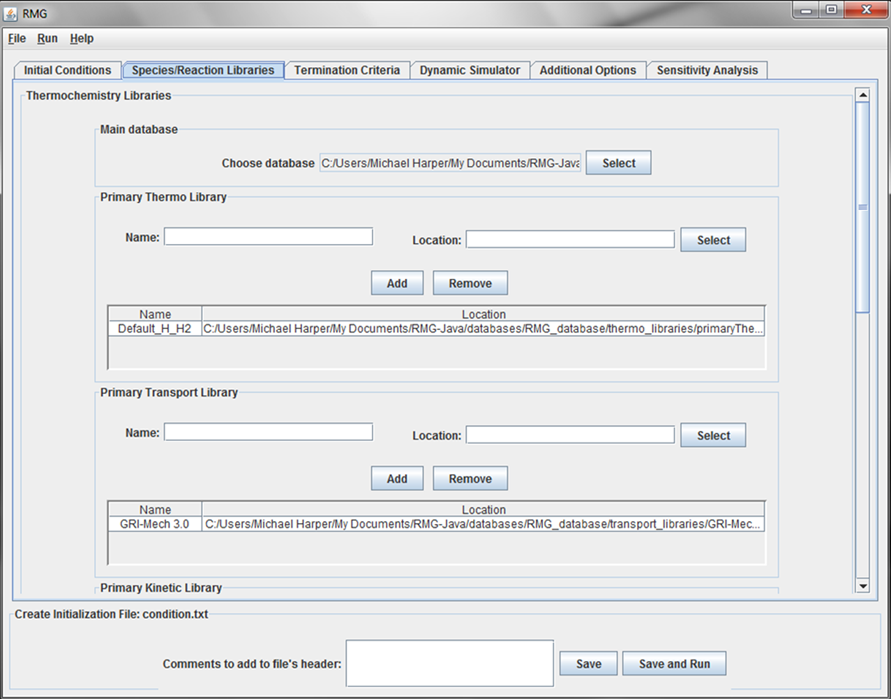
Species/Reactions Libraries tab
This tab of the GUI allows the user to enter the location of the thermochemical libraries RMG will use in building the model.
The default location of the Main Database is the RMG/database/RMG_database folder. We recommend to use the default settings.
The default location of the Primary Thermo Library is the RMG/database/RMG_database/thermo_libraries/primaryThermoLibrary folder. We recommend to include at least this default primary thermochemistry library. To add additional primary thermo libraries: Supply a Name, select the directory by pressing the “Select” button, and then push “Add”.
The default Primary Transport Library is the transport properties reported in the GRI-Mech 3.0 mechanism. If running a pressure-dependent simulation, we recommend including a library that contains small molecules, i.e. C0-C2 species, as the RMG group-additivity approach is more accurate for larger molecules.
To add a Primary Kinetics Library, a Primary Reaction Library, or a Seed Mechanism: Supply a Name, select the directory by pressing the “Select” button, and then push “Add”.
Note
The order of the “Primary Thermo Libraries”, “Primary Transport Library”, “Primary Kinetics Libraries”, “Primary Reaction Library”, and “Seed Mechanisms” in the tables is important. The order established in the table will be conserved when writing the condition.txt file. For any reactions that appear in multiple “Primary Kinetics Libraries” (or “Seed Mechanisms”), RMG will use the information contained in the first “Primary Kinetics Library” (or “Seed Mechanism”) and ignore all others. Similarly, for any species that appear in multiple “Primary Thermo Libraries”, RMG will use the information contained in the first “Primary Thermo Library” and ignore all others.
The “Termination” tab¶
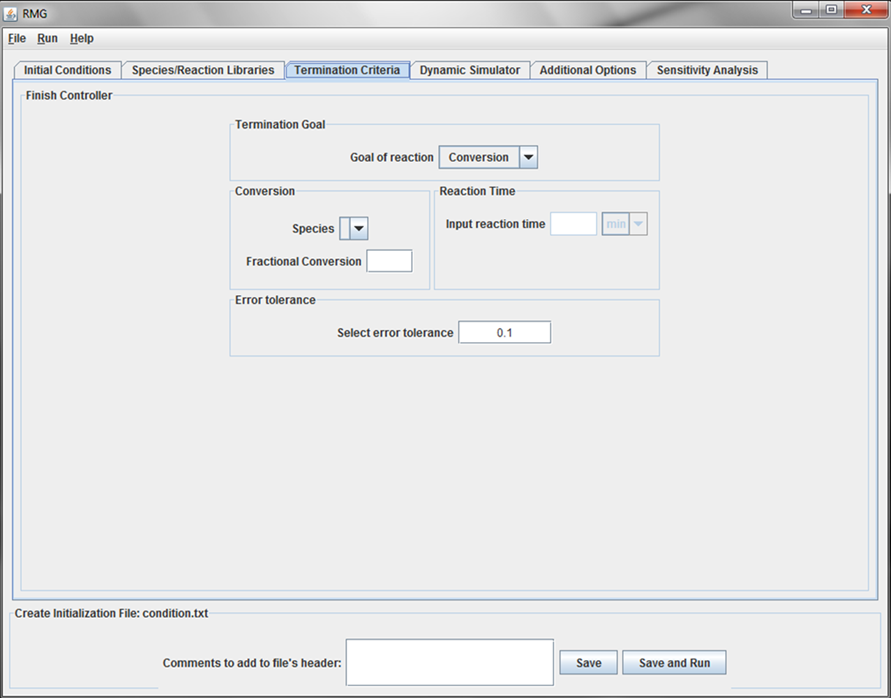
Termination tab
This tab of the GUI allows the user to specify the termination criteria for the model. A user may specify either the desired “ReactionTime” or “Conversion”.
If “Conversion” is selected, the user must specify a species and a fraction conversion (ranging from 0 to 1). The “Species” drop-down menu will only contain the “Reactive-RMG” and “Reactive-User” species specified in the Initialization tab.
If “ReactionTime” is selected, the user must specify the value and units of the desired reaction time.
Lastly, the user must specify an “Error tolerance” for the model. If building a mechanism for a new system, we recommend starting with a high “Error tolerance” (e.g 0.1).
The “Dynamic Simulator” tab¶
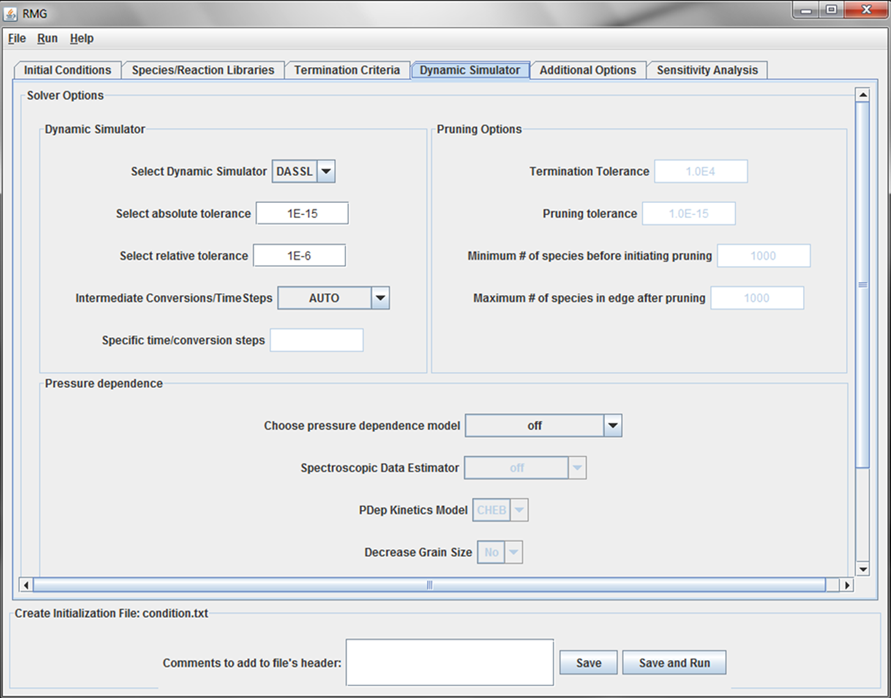
Dynamic Simulator tab
This tab of the GUI allows the user to specify options for:
The ODE Solver¶
The user must select a “Dynamic Simulator” and set the Absolute and Relative Tolerances for that Dynamic Simulator. The user may also select Intermediate times or conversions for RMG to check whether the reaction mechanism needs to be enlarged. We recommend using the automatic time stepping, which is invoked by typing “AUTO” in the “Intermediate” time/conversion fields.
Note
If the user specifies “Intermediate Time Steps,” the values for the “Specific time steps” field must have units of Seconds.
Pruning¶
The user may enable the pruning options by selecting “AUTOPRUNE” in the “Intermediate Conversions/TimeSteps” field. More information for each field in the “Pruning Options” portion of the GUI is located here
The pressure dependence model¶
The user must specify a pressure dependence model. The options are:
- off
- Modified Strong Collision
- Reservoir State
If the user specifies a pressure dependent model, the “Spectroscopic Data Estimator” and “PDep Kinetics Model” fields will be enabled. The only option for the “Spectroscopic Data Estimator” is:
- Frequency Groups
The options for the “PDep Kinetics Model” are:
- CHEB - resulting in Chebyshev polynomials as auxiliary information for pressure-dependent reactions
- PLOG - resulting in Modified Arrhenius parameters at different pressures as auxiliary information for pressure-dependent reactions
- Rate - resulting in no auxiliary information and modified Arrhenius parameters of A 0.0 0.0, where A = k(T,P)
If CHEB or PLOG is selected as the “PDep Kinetics Model”, the fields near the bottom of this tab will become enabled. These fields are optional. However, if data is entered into any of the eight fields, all eight fields must be filled.
The user may also select whether additional energy grains should be included in solving the Master Equation (for pressure-dependent reactions) in the case the calculated k(T,P) is greater than the high-pressure limit rate coefficient.
The “Additional Options” tab¶
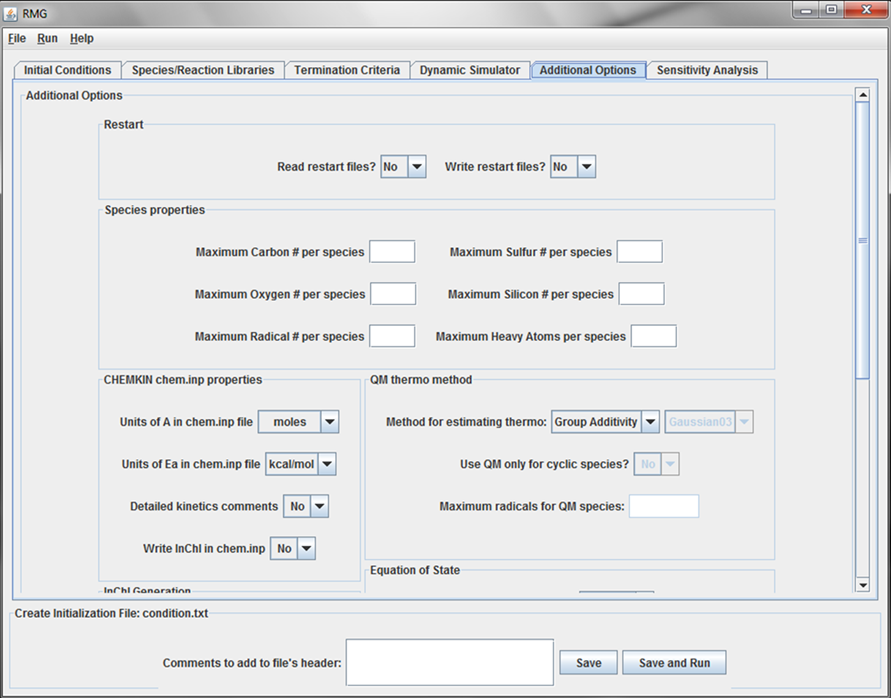
Additional Options tab
This tab allows the user to specify additional (and usually optional) information to RMG.
Restart files¶
The user may choose to read and/or write Restart files. If the “Read restart files” option is turned on, a Restart folder must be present in the working directory.
Species properties¶
The user may choose to override any of the following species properties, by entering data into the appropriate field:
- Maximum carbon number per species
- Maximum oxygen number per species
- Maximum radical number per species
- Maximum sulfur number per species
- Maximum silicon number per species
- Maximum heavy atom (defined as non-hydrogen atoms) per species
The user has the option to enter data for any combination of these fields. If left blank, RMG will use the default values.
CHEMKIN chem.inp properties¶
The next set of fields allow the user to specify the units of the Arrhenius parameters ‘A’ and ‘Ea’ for the chem.inp file generated by RMG. The user may also specify if they want the concise or verbose comments for each reaction in the chem.inp file. Refer to Chemkin options for more details.
Quantum mechanics¶
If the user wishes to compute species thermochemistry using something other than group additivity, e.g. quantum mechanics, select “QM” from the drop-down menu and the remaining fields will become active.
InChI generation¶
The user may also choose to turn off/on the generation of InChIs. If the user chooses to turn InChI generation on, the InChI executable (v 1.01) must be located in the RMG/bin folder.
Equation of State¶
The user currently has only one option for the “Equation of State” field:
- Ideal Gas
Forbidden Structures¶
If the user wishes to specify any forbidden structures, e.g. any alkene (see below), a user-defined name and the associated adjacency list must be supplied.:
Any_Alkene
1 C 0 {2,D}
2 C 0 {1,D}
The “Sensitivity Analysis” tab¶
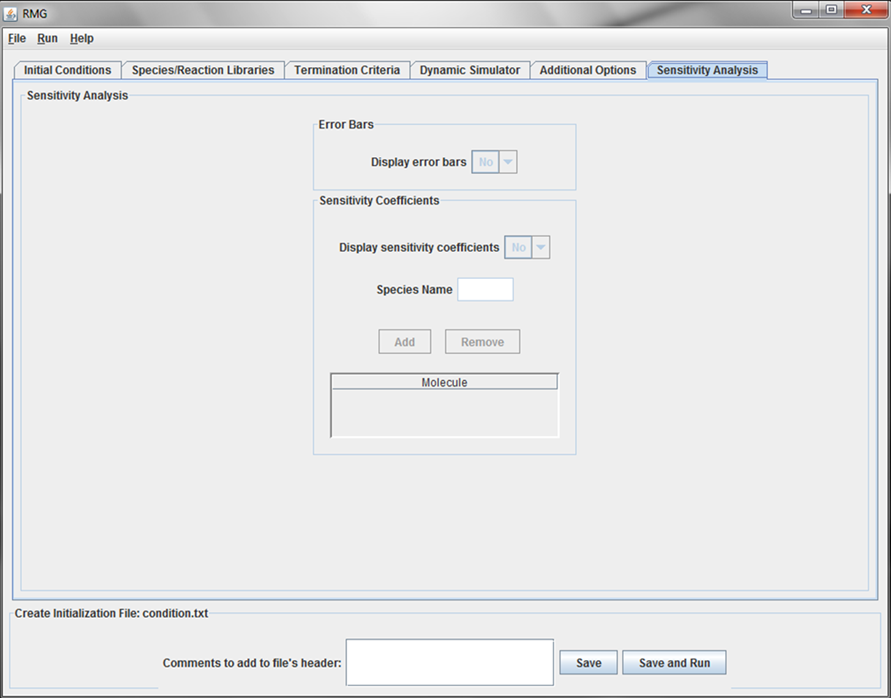
Sensitivity Analysis tab
This tab of the GUI allows the user to specify options for error bars and sensitivity coefficients. The features of this tab will only be active if “DASPK” is selected as the “Dynamic Simulator” on the Dynamic Simulator tab.
The user may turn the generation of error bars “on” or “off.” If turned on, upper and lower error bars will be generated for all species in the model.
The user may also turn the generation of sensitivity coefficients “on” or “off.” The sensitivity coefficients will only be generated for the species listed in the “Molecule” table. The order in which the species appear in the table is not important.
Saving the file¶
To save the file, the user can either press the “Save” button near the bottom of the GUI or by selecting “File” –> “Save” from the navigation toolbar. The file does not have to be named condition.txt. Also, the user may add additional comments to the condition.txt file by adding information to the text field at the bottom of the GUI. These comments will be added to the header of the saved file.
To save and immediately run a file, the user can press the “Save and Run” button near the bottom of the GUI.
Opening a file¶
To open and import the information from an already written condition.txt file, the user can select “File” –> “Open” from the navigation toolbar.
Note
The comments in the header of the file will not be imported.
Running the file¶
To run a file without viewing it, the user can select “Run” –> “Run RMG” from the navigation toolbar.
